Table of Contents
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10 Chapter 13 Notes
Here you will see short notes of the Magnetic effect of electric current for class 10 term 2. This note is specially designed by our expert teacher for your exams and this will brush up your whole chapter in just 2 to 3 minutes.
REVISED SYLLABUS:
Magnetic field, field lines, field due to a current-carrying conductor, field due to current carrying coil or solenoid; Force on the current-carrying conductor, Fleming’s Left Hand Rule, Electric Motor, Electromagnetic induction. The induced potential difference, Induced current. Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule.
DELETED PORTION:
Electric Generator, Direct Current. Alternating current: frequency of AC. Advantage of AC over DC. Domestic Electric Circuit.
What is Magnet?
- Magnet is a substance that attracts iron or iron-like material.
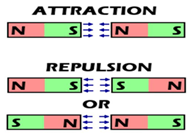
- Magnet has two poles North and South.
- Like poles repel while unlike poles attract each other.
Magnetic field
The area around a magnet in which the force of the magnet can be detected is called its magnetic field.
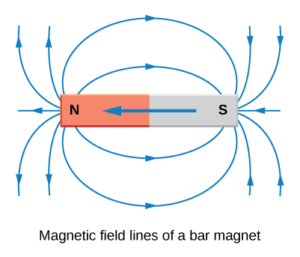
Properties of magnetic field lines
- Magnetic field lines are imaginary lines.
- Field lines form a closed curve.
- The direction of magnetic field lines: – outside the magnet north to south and inside the magnet south to north.
- Magnetic field lines are stronger at poles where they are crowded.
- No two magnetic field lines intersect each other. If they do then it would mean that at the point of intersection there are two directions of the magnetic field which is not possible.
Important Question Of Class 10 Science Chapter 13 for Term 2
Q1. Write any three properties of magnetic field lines? (3 Marks)
Q2. Define magnetic field lines? Why do two magnetic field lines not intersect? (2 Marks)
Magnetic field lines around a current-carrying straight conductor or single circular loop
- It can be represented by a concentric circle at every point.
- The direction of the magnetic field can be given by the Right-hand thumb rule.
Right-Hand Thumb Rule:
Imagine that you are holding a current-carrying conductor in your right hand. If the thumb is pointing towards the direction of current then the finger wrapped around the conductor gives the direction of the magnetic field.
- An increase in current increases the magnetic strength in a straight conductor or single circular loop.
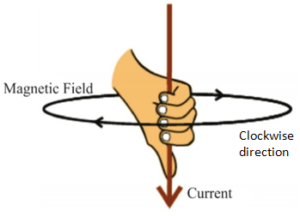
Q3. Explain the right-hand thumb rule? (2 Marks)
Solenoid
A coil with many circular turns of insulated copper wire is called a solenoid.
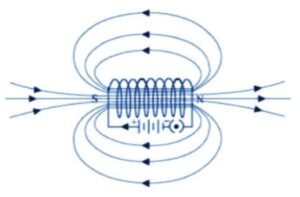
Magnetic field around a current-carrying solenoid
One end of the solenoid behaves like a north pole and the other as a South pole therefore magnetic field due to current in the solenoid is similar to a bar magnet.
The strength of the magnetic field of a solenoid can be increased by-
- Increasing the amount of current.
- Increasing the number of turns.
Use- Solenoids can be used to magnetize material like soft iron.
Q4. What is a solenoid? How can we increase the magnetic field around a solenoid? (3 Marks)
Difference between Fleming’s left-hand rule and Fleming’s right-hand rule?
|
Fleming left-hand rule |
Fleming right-hand rule |
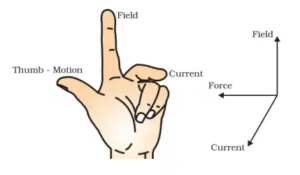
| 1. Stretch the thumb forefinger and middle finger of the left hand so that they are perpendicular to each other.
2. If the forefinger indicates the direction of the magnetic field, middle finger indicates the direction of current then the thumb gives us the direction of motion of force acting on the conductor. Use in the electric motor. |
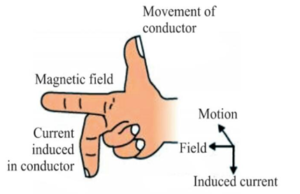
1. Stretch the thumb forefinger and middle finger of the right hand so that they are perpendicular to each other.
2. If the forefinger indicates the direction of the magnetic field thumb indicates the direction of motion of the conductor then the middle finger gives us the direction of induced current in the conductor. Use in an electric generator. |
|
|
|
Q5. State Fleming’s left-hand rule? (2 Marks)
Q6. State Fleming’s right-hand rule? (2 Marks)
Electric motor
The electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy.
Principle of electric motor
- It works on the principle of the magnetic effect of electric current.
- When a current-carrying rectangular coil is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field then it experiences a force that rotates it continuously in a direction given by Fleming’s left-hand rule.
The function of the main part of the electric motor
- Armature-Armature coil carrying current placed perpendicular to the magnetic field, as a result, it experiences an equal force in the mutually opposite direction.
- Brushes-It connects current from the battery to split ring.
- Split ring- It Reverses the direction of current in the coil from brushes after each half rotation.
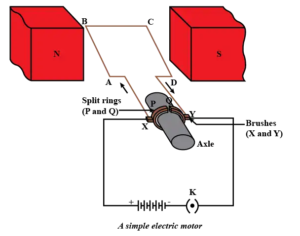
Q7. Write the principle of working of an electric motor? (1 Marks)
Q8. Explain the function of (a) Armature (b) Brushes (c) Split ring of an electric motor? (3 Marks)
Class 10 Chapter 13 Notes Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Electromagnetic induction
The phenomenon of the production of induced current in a coil, placed in changing magnetic field is called electromagnetic induction. The direction of the induced current is given by Fleming’s right-hand rule.
Q9. What do you mean by Electromagnetic induction? (1 Marks)
If you have any doubt about these notes of Magnetic Effects of Electric Current then go to our Youtube channel Academic Excellence in School and watch the related video. Also if you are preparing for MCQs question of class 10 or competitive question of class 10. Then click on the below links to practice questions and answer.
Class 10 Science chapter wise important MCQ in English Medium
Class 10 विज्ञान Chapter-wise Important MCQ Hindi Medium
Class 10 social science chapter wise important MCQ
Class 10 सामाजिक विज्ञान Chapter-wise MCQ
Class 10 Maths Chapter-Wise Important MCQs